Introduction on Sociology Definition & Scope
Sociology is a dynamic and evolving social science that seeks to understand human behavior, social relationships, and societal structures. It examines how individuals interact within groups, institutions, and cultures, and how these interactions shape and are shaped by broader social forces. As a discipline, sociology provides critical insights into social issues such as inequality, crime, education, religion, and politics.
This article explores the Sociology Definition, its key perspectives, and its scope in analyzing and interpreting social phenomena. We can better appreciate sociology’s applicability in tackling today’s societal issues if we comprehend its fundamental ideas and applications.
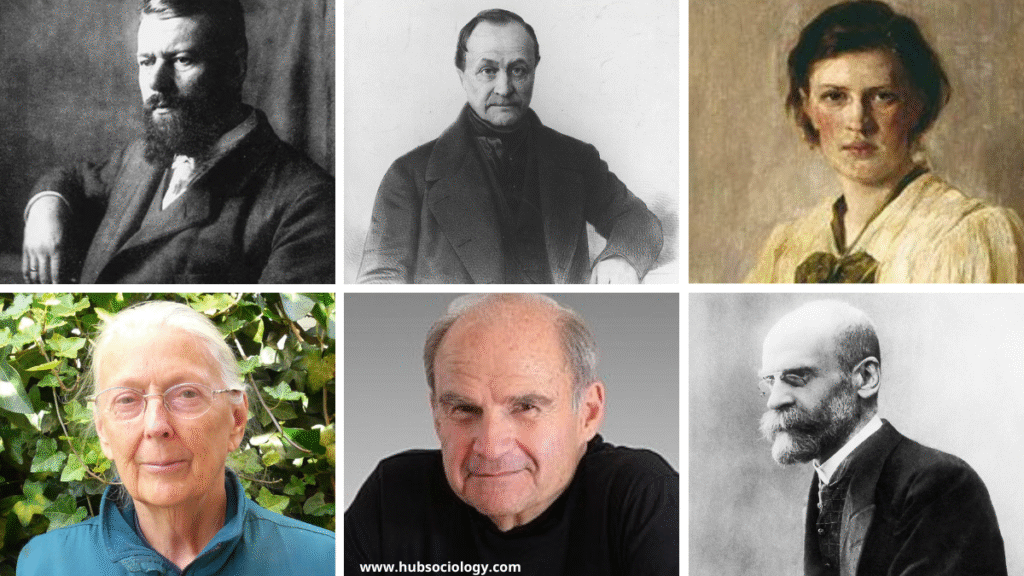

Table of Contents
Sociology Definition
The word sociology comes from the Latin word socius, which means companion, and the Greek word logos, which means study. Thus, the precise definition of sociology is the study of friendship or social relationships.
Classical Sociology Definition
- Auguste Comte (1798–1857) – According to Comte, who is frequently referred to as the “Father of Sociology,” sociology is the scientific study of society.
- Emile Durkheim (1858–1917) – Durkheim viewed sociology as the study of social facts—patterns of behavior that exert external control over individuals, such as laws, norms, and institutions.
- Max Weber (1864–1920) – Weber focused on interpretive sociology (Verstehen), arguing that understanding human actions requires examining the subjective meanings individuals attach to their behavior.
- Karl Marx (1818–1883) – Marx analyzed society through the lens of class struggle, emphasizing economic structures and power dynamics in shaping social relations.
Modern Sociology Definition
Contemporary sociologists define sociology as:
- “The systematic study of human society and social interactions.” (Giddens, 2009)
- “The scientific analysis of social patterns, institutions, and processes.” (Macionis, 2018)
Sociology differs from other social sciences (like psychology or economics) by focusing on group behavior, social structures, and systemic influences rather than individual actions or market dynamics.
Key Perspectives in Sociology
Sociologists employ various theoretical perspectives to analyze social phenomena. The three major paradigms are:
1. Structural-Functionalism (Macro Perspective)
- Key Thinkers: Emile Durkheim, Talcott Parsons, Robert Merton
- Core Idea: Society is a complex system with interrelated parts that work together to maintain stability and social order.
- Concepts:
- Religion, education, and the family are examples of social institutions that play vital roles.
- Manifest functions (intended consequences) vs. latent functions (unintended consequences).
- Social solidarity (mechanical vs. organic solidarity, as per Durkheim).
Criticism: Overemphasizes harmony and ignores social conflicts and inequalities.

2. Conflict Theory (Macro Perspective)
- Key Thinkers: Karl Marx, Max Weber, C. Wright Mills
- Core Concept: Power struggles and disparities based on gender, race, class, and other categories define society.
- Concepts:
- Class struggle (bourgeoisie vs. proletariat in capitalism).
- Domination and power (Weber’s classification of authority: legal-rational, charismatic, and traditional).
- Ideological control: To preserve power, the ruling class manipulates cultural myths.
Criticism: Overlooks social cohesion and cooperation; seen as overly deterministic.
3. Symbolic Interactionism (Micro Perspective)
- Key Thinkers: George Herbert Mead, Herbert Blumer, Erving Goffman
- Core Idea: Society is constructed through everyday interactions and shared meanings.
- Concepts:
- Symbols (language, gestures, signs shape social reality).
- Social construction of reality (people create meaning through interactions).
- Dramaturgical approach (Goffman’s view of social life as a theatrical performance).
Criticism: Neglects larger structural forces; too focused on individual agency.
Scope of Sociology
Sociology covers a vast range of topics, from micro-level interactions to macro-level institutions. Its scope can be categorized into:
1. Theoretical Sociology
- Develops frameworks to explain social behavior (e.g., functionalism, conflict theory, feminism).
- Examines concepts like socialization, deviance, and social change.
2. Applied Sociology
- Uses sociological research to address real-world problems (e.g., policy-making, social work, criminology).
- Fields include medical sociology, urban sociology, and environmental sociology.
3. Major Areas of Study
- Social Institutions: Family, education, religion, economy, politics.
- Social Stratification: Class, race, gender, caste inequalities.
- Social Change: Globalization, technology, social movements.
- Criminology & Deviance: Causes of crime, societal reactions.
- Media and Culture: Influence of media, subcultures, and cultural standards.
4. Research Methods
Sociologists use both quantitative (surveys, statistics) and qualitative (interviews, ethnography) methods to study social phenomena.
Importance of Sociology
- Understanding Social Issues: Helps analyze poverty, racism, gender discrimination, and crime.
- Policy Development: Informs government and NGO interventions.
- Promoting Social Justice: Highlights inequalities and advocates for marginalized groups.
- Global Perspective: Examines transnational issues like migration, climate change, and terrorism.
Conclusion on Sociology Definition & Scope
A crucial field that offers profound understanding of social systems and human behavior is sociology. By employing various theoretical perspectives and research methods, sociologists uncover the complexities of social life and contribute to solving pressing social issues. Its broad scope—from individual interactions to global systems—makes sociology indispensable in understanding and improving the world we live in.
As societies continue to evolve, sociology remains a crucial tool for fostering social awareness, equity, and sustainable development.
Do you like this this Article ? You Can follow as on :-
Facebook – https://www.facebook.com/hubsociology
Whatsapp Channel – https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029Vb6D8vGKWEKpJpu5QP0O
Gmail – hubsociology@gmail.com
Topic Related on Sociology Definition & Scope Questions
5-Mark Questions on Sociology Definition & Scope (Short Answer Type)
- Define sociology and name its founding thinkers.
- What is the significance of Auguste Comte in sociology?
- Differentiate between manifest and latent functions in structural-functionalism.
- Explain Karl Marx’s concept of class struggle.
- What is symbolic interactionism? Give an example.
- List any three key areas of study in sociology.
- How does sociology differ from psychology?
- What is the dramaturgical approach in sociology?
- Name two research methods used in sociology.
- Why is sociology important in understanding social issues?
10-Mark Questions on Sociology Definition & Scope (Brief Essay Type)
- Discuss the key contributions of Emile Durkheim to sociology.
- Compare and contrast structural-functionalism and conflict theory.
- Explain Max Weber’s concept of Verstehen and its role in sociology.
- How does sociology help in analyzing social inequality? Provide examples.
- Discuss the scope of sociology in studying culture and media.
- What are the major theoretical perspectives in sociology? Explain any one in detail.
- How do social institutions (e.g., family, education) contribute to societal stability?
- Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of symbolic interactionism.
- Why is applied sociology important? Discuss its real-world applications.
- Explain the relationship between sociology and other social sciences (e.g., economics, political science).
15-Mark Questions on Sociology Definition & Scope (Long Essay Type)
- Define sociology and discuss its nature and scope in detail.
- Critically examine the structural-functionalist perspective in sociology with suitable examples.
- Analyze Karl Marx’s conflict theory and its relevance in contemporary society.
- What is the role of sociology in understanding and addressing global social issues (e.g., migration, climate change)?
- Discuss the importance of research methods in sociological studies. Compare quantitative and qualitative approaches.
- How do symbolic interactionists explain the construction of social reality? Provide examples.
- Evaluate the contributions of classical sociologists (Comte, Durkheim, Marx, Weber) to the development of sociology.
- How does sociology contribute to policy-making and social reform? Explain with case studies.
- Discuss the impact of globalization on social structures from a sociological perspective.
- “Sociology is not just an academic discipline but a tool for social change.” Justify this statement.

1 thought on “Sociology Definition & Scope – Understanding the Discipline”