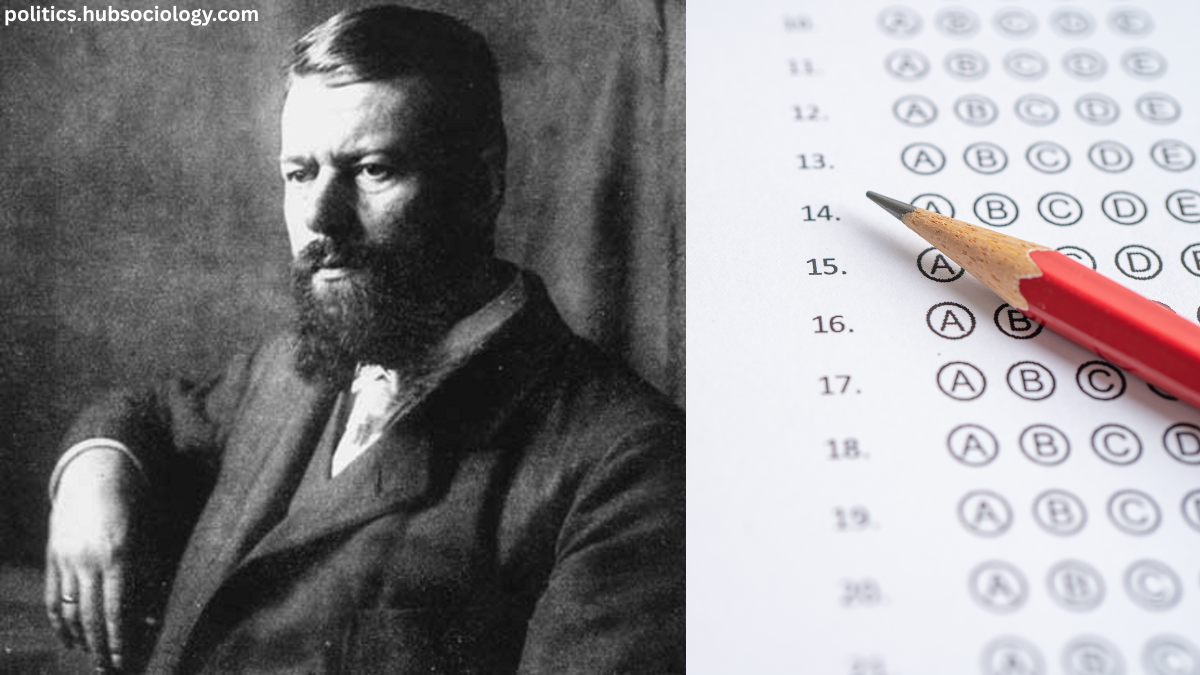Max Weber, a founding figure of modern sociology, is renowned for his profound contributions to social theory, religion, bureaucracy, and rationalization. Unlike Karl Marx, who emphasized economic determinism, Weber argued that culture, ideas, and religion play crucial roles in shaping societies. His seminal work, The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism (1905), explores how Calvinist beliefs fostered the rise of modern capitalism by promoting hard work, discipline, and reinvestment of profits.
Max Weber introduced key concepts such as:
- Verstehen (interpretive sociology) – Understanding social behavior through subjective meanings.
- Types of authority (Traditional, Charismatic, Legal-Rational) – Explaining power structures.
- Bureaucracy & Rationalization – Analyzing the efficiency and dehumanization in modern institutions.
- Social Stratification (Class, Status, Party) – Expanding beyond Marx’s economic class model.
His comparative studies on world religions (Christianity, Hinduism, Confucianism, Judaism) revealed how cultural values influence economic systems. Weber’s “Iron Cage” metaphor warns of modernity’s impersonal, rule-bound systems stifling human freedom. His interdisciplinary approach bridges history, economics, and sociology, making him indispensable for UGC NET Sociology and beyond.
Max Weber – MCQ for UGC NET Sociology
1. Max Weber was a pioneer of:
a) Conflict Theory
b) Symbolic Interactionism
c) Verstehen (Interpretive Sociology)
d) Structural Functionalism
Answer: c) Verstehen (Interpretive Sociology)
2. Weber’s concept of “Rationalization” refers to:
a) The decline of magic and tradition in modern society
b) The increasing dominance of efficiency, calculability, and control in social life
c) The rise of communism
d) The spread of religious fundamentalism
Answer: b) The increasing dominance of efficiency, calculability, and control in social life
3. Weber’s famous work “The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism” explores:
a) The role of Hinduism in economic development
b) How Calvinist beliefs contributed to the rise of capitalism
c) The impact of Buddhism on industrialization
d) The decline of feudalism
Answer: b) How Calvinist beliefs contributed to the rise of capitalism
4. According to Weber, the “Iron Cage” refers to:
a) A prison system in modern society
b) The dehumanizing effects of bureaucratic rationality
c) The constraints of feudal society
d) The rigidity of religious doctrines
Answer: b) The dehumanizing effects of bureaucratic rationality
5. Weber’s theory of social stratification includes:
a) Only economic factors (class)
b) Class, Status, and Party (Power) as three dimensions
c) Only caste-based divisions
d) Only gender inequalities
Answer: b) Class, Status, and Party (Power) as three dimensions
6. Which of the following is NOT a type of authority according to Weber?
a) Traditional Authority
b) Charismatic Authority
c) Legal-Rational Authority
d) Feudal Authority
Answer: d) Feudal Authority
7. Weber’s concept of “Bureaucracy” includes:
a) Hierarchy, written rules, and impersonality
b) Family-based decision-making
c) Emotional decision-making
d) Decentralized power structures
Answer: a) Hierarchy, written rules, and impersonality

8. What is “Verstehen” in Weber’s methodology?
a) Statistical analysis of social facts
b) Understanding social action through interpretation
c) Experimental research
d) Historical materialism
Answer: b) Understanding social action through interpretation
9. Weber argued that capitalism originated first in:
a) India
b) China
c) Western Europe
d) Africa
Answer: c) Western Europe
10. Weber’s “Ideal Type” is:
a) A perfect representation of reality
b) A conceptual tool to analyze social phenomena
c) A statistical average
d) A moral guideline for society
Answer: b) A conceptual tool to analyze social phenomena
11. Which religion did Weber associate with the rise of capitalism?
a) Hinduism
b) Islam
c) Protestantism (Calvinism)
d) Buddhism
Answer: c) Protestantism (Calvinism)
12. Weber’s study of religion included all EXCEPT:
a) The Communist Manifesto
b) The Protestant Ethic
c) The Religion of India
d) Ancient Judaism
Answer: a) The Communist Manifesto
13. According to Weber, modern capitalism is driven by:
a) Rational calculation and profit-making
b) Religious rituals
c) Feudal obligations
d) Emotional impulses
Answer: a) Rational calculation and profit-making
14. Weber’s view on Marx’s theory was that:
a) He completely agreed with Marx
b) He acknowledged economics but emphasized culture and ideas
c) He rejected all of Marx’s ideas
d) He focused only on class struggle
Answer: b) He acknowledged economics but emphasized culture and ideas
15. Which of the following is a characteristic of charismatic authority?
a) It is based on written laws
b) It is based on personal charm and extraordinary qualities
c) It is hereditary
d) It is impersonal
Answer: b) It is based on personal charm and extraordinary qualities
16. Weber’s concept of “Social Action” includes all EXCEPT:
a) Instrumentally rational action
b) Value-rational action
c) Affective action
d) Instinctive action
Answer: d) Instinctive action
17. Which of the following best describes “Value-Rational Action”?
a) Action driven by emotional impulses
b) Action guided by conscious belief in intrinsic value (e.g., religious or ethical motives)
c) Action based on habit or tradition
d) Action aimed at maximizing profit
Answer: b) Action guided by conscious belief in intrinsic value
18. According to Weber, which type of authority is most stable in modern societies?
a) Traditional authority
b) Charismatic authority
c) Legal-rational authority
d) Feudal authority
Answer: c) Legal-rational authority
19. Weber’s study “The Religion of China” focused on:
a) Why Confucianism did not lead to capitalism
b) The impact of Buddhism on trade
c) The rise of Protestantism in China
d) The decline of feudalism
Answer: a) Why Confucianism did not lead to capitalism
20. Which of the following is a critique of Weber’s “Protestant Ethic” thesis?
a) Capitalism existed before Protestantism
b) Weber ignored economic factors completely
c) He overemphasized Hinduism’s role
d) He did not study Judaism
Answer: a) Capitalism existed before Protestantism
21. Weber’s “Ancient Judaism” explored:
a) The rise of capitalism in Israel
b) How Jewish ethics influenced Western rationalism
c) The decline of Jewish authority
d) The impact of Judaism on feudalism
Answer: b) How Jewish ethics influenced Western rationalism
22. Which of these is NOT a feature of Weber’s “Ideal Type” bureaucracy?
a) Hierarchy of authority
b) Written rules and regulations
c) Personal relationships in decision-making
d) Specialization of labor
Answer: c) Personal relationships in decision-making
23. Weber’s “The Sociology of Religion” argues that religion:
a) Has no impact on economic behavior
b) Can shape economic systems and social structures
c) Is irrelevant in modern societies
d) Only affects political systems
Answer: b) Can shape economic systems and social structures

24. According to Weber, the “Spirit of Capitalism” emphasizes:
a) Hard work, frugality, and reinvestment of profits
b) Luxury consumption and leisure
c) Religious rituals without economic impact
d) Feudal loyalty
Answer: a) Hard work, frugality, and reinvestment of profits
25. Weber’s concept of “Party” in stratification refers to:
a) Political parties in democracy
b) Organized groups seeking power and influence
c) Social class divisions
d) Religious sects
Answer: b) Organized groups seeking power and influence
26. Which of the following is an example of “Traditional Authority”?
a) A CEO elected by shareholders
b) A king ruling by hereditary right
c) A revolutionary leader
d) A bureaucrat following written laws
Answer: b) A king ruling by hereditary right
27. Weber’s methodology emphasizes:
a) Interpretive understanding (Verstehen)
b) Only quantitative data
c) Experimental methods
d) Historical materialism
Answer: a) Interpretive understanding (Verstehen)
28. Weber’s view on bureaucracy was that it is:
a) Always inefficient
b) Highly efficient but dehumanizing
c) Only relevant in feudal societies
d) Based on emotional decisions
Answer: b) Highly efficient but dehumanizing
29. Which of these is a characteristic of “Charismatic Authority”?
a) It is based on legal codes
b) It is unstable and depends on the leader’s personal appeal
c) It is inherited
d) It follows strict bureaucratic rules
Answer: b) It is unstable and depends on the leader’s personal appeal
30. Weber’s “The City” discusses:
a) The role of urban centers in social and economic development
b) The decline of rural societies
c) The impact of religion on cities
d) Only ancient Greek cities
Answer: a) The role of urban centers in social and economic development
31. According to Weber, modern capitalism differs from earlier forms because it is based on:
a) Rational calculation and systematic profit-making
b) Religious donations
c) Feudal obligations
d) Barter systems
Answer: a) Rational calculation and systematic profit-making
32. Weber’s concept of “Class” is primarily based on:
a) Economic position and market relations
b) Caste hierarchy
c) Religious affiliation
d) Political party membership
Answer: a) Economic position and market relations
33. Which of the following best describes “Affective Action”?
a) Action based on logical reasoning
b) Action driven by emotions (e.g., love, anger)
c) Action following traditions
d) Action for maximizing profit
Answer: b) Action driven by emotions
34. Weber argued that the “Disenchantment of the World” refers to:
a) The decline of magical thinking due to rationalization
b) The rise of religious fundamentalism
c) The end of capitalism
d) The fall of feudal systems
Answer: a) The decline of magical thinking due to rationalization
35. In Weber’s view, which factor is crucial for the rise of modern capitalism?
a) A cultural shift (Protestant ethic) alongside economic conditions
b) Only technological advancements
c) Government policies alone
d) The decline of cities
Answer: a) A cultural shift (Protestant ethic) alongside economic conditions
36. Weber’s “Economy and Society” is a foundational text on:
a) Sociological theory, authority, and bureaucracy
b) Only economic systems
c) Psychological behavior
d) Ancient history
Answer: a) Sociological theory, authority, and bureaucracy
37. Which of these is NOT a type of social action in Weber’s framework?
a) Instrumentally rational
b) Traditional
c) Instinctive
d) Value-rational
Answer: c) Instinctive
38. Weber’s analysis of Hinduism concluded that:
a) Its otherworldly focus hindered capitalist development
b) It promoted capitalism like Protestantism
c) It had no impact on the economy
d) It was identical to Calvinism
Answer: a) Its otherworldly focus hindered capitalist development
39. Which of the following best describes Weber’s view on Marxism?
a) He agreed with Marx on class but added status and party
b) He completely rejected Marx
c) He ignored economic factors
d) He focused only on revolution
Answer: a) He agreed with Marx on class but added status and party
40. Weber’s “Methodology of the Social Sciences” emphasized:
a) Value neutrality and objective analysis
b) Only subjective interpretations
c) Religious bias in research
d) Ignoring historical context
Answer: a) Value neutrality and objective analysis
41. Which type of authority is most likely to undergo “routinization of charisma”?
a) Traditional
b) Charismatic
c) Legal-rational
d) Feudal
Answer: b) Charismatic
42. Weber’s concept of “Status Group” refers to:
a) Social honor and prestige, independent of class
b) Only economic stratification
c) Political power alone
d) Religious sects
Answer: a) Social honor and prestige, independent of class
43. According to Weber, bureaucracy is:
a) The most efficient form of organization but can be oppressive
b) Always corrupt
c) Only found in governments
d) Based on personal favors
Answer: a) The most efficient form of organization but can be oppressive

44. Weber’s “The Protestant Sects and the Spirit of Capitalism” argues that:
a) Religious communities enforced disciplined economic behavior
b) Only Catholics contributed to capitalism
c) Sects had no economic impact
d) Capitalism emerged without religious influence
Answer: a) Religious communities enforced disciplined economic behavior
45. Which of these is a key difference between Marx and Weber?
a) Weber emphasized ideas and culture; Marx focused on material conditions
b) Weber rejected all forms of authority
c) Marx ignored class struggle
d) Weber supported communism
Answer: a) Weber emphasized ideas and culture; Marx focused on material conditions
46. Weber’s “The Rational and Social Foundations of Music” shows his interest in:
a) The sociology of art and cultural rationalization
b) Only economic history
c) Political revolutions
d) Religious dogmas
Answer: a) The sociology of art and cultural rationalization
47. Which of the following is a limitation of Weber’s bureaucracy theory?
a) It underestimates informal networks and human agency
b) It ignores hierarchy
c) It rejects all forms of authority
d) It only applies to feudal systems
Answer: a) It underestimates informal networks and human agency
48. Weber’s “Science as a Vocation” discusses:
a) The role of intellectuals and value-neutral research
b) The decline of science
c) Only technological advancements
d) Religious miracles
Answer: a) The role of intellectuals and value-neutral research
49. Which concept did Weber use to compare world religions?
a) Theodicy
b) Dialectical materialism
c) False consciousness
d) Alienation
Answer: a) Theodicy
50. Weber’s work is most associated with which sociological tradition?
a) Interpretive sociology
b) Structural functionalism
c) Conflict theory (Marxist)
d) Feminist theory
Answer: a) Interpretive sociology
Do you like this this Article ? You Can follow as on :-
Facebook – https://www.facebook.com/hubsociology
Whatsapp Channel – https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029Vb6D8vGKWEKpJpu5QP0O
Gmail – hubsociology@gmail.com